A bursa is a sac of synovial fluid, rich in protein and collagen, that acts as a cushion to protect soft tissue, such as tendons, ligaments and muscle, from friction and excess pressure. We have over 150 bursae (plural for bursa) in our bodies with most of them located in our joints.
Bursitis, by definition, is the inflammation or irritation of a bursa sac. When the bursa becomes swollen, the sac itself can develop little tears and may cause tears to the surrounding soft tissue. In some cases, the inflamed bursa also becomes infected with bacteria (referred to as septic bursitis) and it is necessary to see a doctor to get rid of the infection.
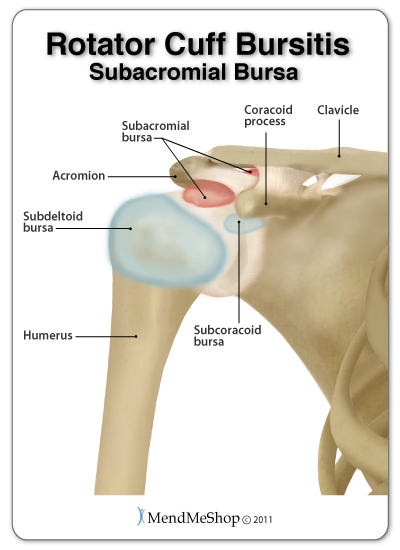
There are 3 main bursae around the rotator cuff. The subacromial bursa protects the supraspinatus tendon from the coracoid process and acromion. The subcoracoid bursa lies between the coracoid process and the joint capsule. The subdeltoid bursa lies under the deltoid muscle, cushioning it from the bones in the shoulder joint capsule. Often the subdeltoid and subacromial bursa are connected around the rotator cuff.
The subacromial bursa is the bursa in the shoulder that is most commonly affected by bursitis. It acts as a cushion to allow the supraspinatus tendon to slide smoothly over the neighboring soft tissue and bone. Due to its location and relationship to the acromion and supraspinatus, the subacromial bursa tends to be most at risk of being impinged or irritated.
Shoulder bursitis is often connected to impingement syndrome and rotator cuff tendonitis. For this reason, it is always wise to address and treat shoulder pain as soon as possible so that the problem doesn't get worse. A healthy subacromial bursa is usually about the size of a small plum, but can swell to the size of an orange when bursitis sets in. This is what creates the soft tissue damage or possible impingement in the shoulder joint.
The most common symptom is experiencing pain when lifting overhead. This is because the head of the humerus is compressing the swollen bursa against the glenohumeral joint and the underside of the acromion. If you have pain when lifting over head, however, it could indicate one or more soft tissue injuries in the shoulder. Subacromial bursitis is very often diagnosed alongside other rotator cuff problems or impingement syndrome.
If you are suffering or have suffered from other shoulder problems such as rotator cuff tendonitis, bone spurs, a hooked acromion, and/or impingement syndrome your subacromial bursa is at risk of becoming inflamed. These conditions can irritate the bursa which will result in bursitis if left untreated.
Repetitive overhead shoulder movements, especially if they are weight bearing, may cause fatigue or general weakness in the shoulder muscles and tendons. As a result, your shoulder joint could become misaligned causing more pressure on the subacromial bursa.
Calcification of the bursa sac can also cause inflammation from within the bursa.
If you are suffering from inflammation of the subacromial bursa, you may be experiencing the following symptoms:
It is important to treat bursitis in the early stages to reduce the symptoms, minimize damage and maintain motion and strength in your arm and shoulder. Resting your shoulder and reducing any activities that add pressure on your bursa will help to reduce your pain and bursitis inflammation. By treating your rotator cuff bursitis in the early stages with Cold Compression and Circulation Boost, you are more likely to prevent long-term damage and chronic conditions from setting in.
Visiting your doctor when you have shoulder pain is always recommended, as there are many possible issues that can happen within the shoulder. Sometimes, one set of symptoms can result in multiple diagnoses. An X-Ray and MRI are often needed in order to diagnose a shoulder ailment properly.
Although rare, subacromial bursitis can be caused by an infection which is potentially very serious. Your doctor will be able to rule this out as a possible cause.
You doctor will likely do some range of motion tests with you, and may refer you on to a physical therapist. Many people see great improvements in physical therapy with shoulder related problems and are able to treat the problem with conservative measures.
A sign that you may have subacromial bursitis is acute pain when trying to reach the affected arm behind you towards the lower back, as if to get something out of your back pocket. You would also experience pain when reaching above your head, as you would when putting something on a high shelf. If you feel sharp pain with both of these motions you may have shoulder bursitis and/or other related conditions and should see a doctor.
(NSAIDs - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can be used if required to help manage your pain. However, these aren't recommended for long term use, as they can cause gastrointestinal difficulties and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. The use of cold therapy and Circulatory Boost in conjunction with NSAIDs can greatly improve the effect of this medication and can help to heal quicker.
Your doctor may aspirate the inflamed bursa. This involves removing the extra fluid that has built up with a needle. Sometimes, the fluid will be tested at a laboratory to rule out infection.
If your bursitis does not get better with conservative treatments, a subacromial decompression may be done. It is an arthroscopic procedure, so tine incisions are made and a pencil-sized camera is inserted into the shoulder. A small shaver is inserted into another incision, and is used to remove the swollen bursa all together. The surgeon will then look for any damage to the rotator cuff. If the subacromial space is small, the surgeon may use a burr to shave the acromion down in order to create more space for the rotator cuff tendons. This is also done to remove any bone spurs in the shoulder.
Recovery time for the surgery will depend a number of different factors including your healing ability, diet, rest and how many procedures were done in your surgery. Your doctor will advise you on your recovery, and will let you know if/when physical therapy can be started.
Relieving the symptoms of bursitis initially focuses on keeping the pressure off the bursa (i.e. carrying a backpack or purse on the opposite shoulder). Surgery may be required if your bursa irritation is a result of a bone formation problem, such as a hooked acromion causing impingement of the bursa. If your bursitis is caused by an infection (septic bursitis), the doctor will probably drain the bursa sac with a needle and perscribe antibiotics to treat the infection.
For non-infectious bursitis, the preliminary treatment starts with non-operative options such as rest and cold therapy (use a Cold Compress or Ice Pack to reduce swelling and inflammation. Surgery to remove the inflamed bursa is normally not required for bursitis, however if you fail to see improvement with the conservative treatments, your physician may recommend surgery to remove the bursa completely. Although this removes the problem of an inflamed bursa, you are left with less cushioning in your rotator cuff which can lead to a host of other shoulder pain and problems.
The most important factor in healing bursitis is resting your shoulder. This can be difficult when you have to carry on with daily activities, but resting your shoulder whenever you can is recommended. During your recovery you will probably have to modify or avoid the activities that stress your bursa until your pain and inflammation settle.
Treatments should involve decreasing swelling, relieving stress on the shoulder, correcting any biomechanical dysfunction (hooked acromion, bone spur, etc.), treating scar tissue, and then restoring strength and movement in your shoulder.
To decrease inflammation and relieve the pain of rotator cuff bursitis doctor's recommend cold therapy.
Applying cold to your inflamed bursa will help decrease the swelling and redness around it. Cold therapy will also help to numb the pain in your shoulder and rotator cuff and help to control the inflammation.
Cooling your inflamed subacromial bursa as needed throughout the day, for approximately 15 - 20 minutes at a time, is recommended. Do not apply ice directly on your skin, rather wrap it in a cloth or towel or, better yet, use a cold wrap that fits easily and comfortably to your body.
Applying cold to your tender bursa and rotator cuff is the first step in treating your bursitis. Then begin Circulatory Boost treatments through use of the TShellz Wrap® to continue the healing process.
After severe inflammation and swelling is reduced you can really start to work on enhancing blood flow to the shoulder area through the use of a shoulder TShellz Wrap®. The TShellz Wrap® increases the amount of blood that flows naturally to tissue in your shoulder to nourish the area and help maximize the ability of the body to work on healing tissue.
Bursae naturally receive very little blood supply and when you stop moving your shoulder because it hurts the blood flow is reduced even further, limiting your body's natural ability to heal itself.
By treating your bursa with Circulatory Boost you can increase your body's blood supply to the shoulder and increase your body's natural healing power.
A Shoulder TShellz Wrap® is the tool you need to treat your sore shoulder because it speeds healing and relaxes the surrounding muscles, tendons and ligaments. Through a process we call Circulation Boost, soft tissue in the shoulder are safely and gently stimulated. Your body responds with a rapid increase in blood flow to the area, increasing the supply of oxygen and nutrients to injured tissue to promote healing. Our Shoulder TShellz Wrap® provides effective, non-invasive, non-addictive pain relief and healing with no side effects.
Enhanced blood flow from a TShellz Wrap® treatment whisks away dead tissue and toxins that have built up from your damaged rotator cuff. When you stop moving your arm and shoulder due to shoulder pain, your muscles and other tissue can become weaker and dead tissue and toxins in the area can cause further tissue deterioration - this can lead to atrophy. By clearing the area of toxins and increasing the amount of oxygen and nutrients to your muscle and other tissue, the risk of atrophy (muscle weakness and/or deterioration) is greatly reduced. Keeping your upper arm, shoulder and rotator cuff tissue as healthy as possible throughout the healing process will allow you to improve shoulder strength again once your pain has gone and your bursa has healed.
Not only does the incorporation of conservative treatments (such as the use of a Cold Compress or Ice Pack and the Shoulder TShellz Wrap®) aid in your home recovery process, but it helps to prevent long term complications. Pain, lack of mobility, tendinosis, or a complete tendon rupture are some of the more common long term complications that can occur when rotator cuff tendinitis, tendon tears, and other injuries go untreated. By treating your rotator cuff with these treatments, you can keep your joint limber and reduce the risk/frequency of re-injury - helping reducing the risk of chronic problems in the future.
With these simple and safe home treatment therapies - a Cold Compress or Ice Pack + Shoulder TShellz Wrap® treatments, you will notice significantly reduced pain and an significant improvement in the healing speed of your injured bursae.
We recommend that you consult your doctor and/or physiotherapist before using any of our outstanding products, to make sure they're right for you and your condition.
Click HERE to Go To Our Online Store We take all major credit cards and Paypal.
If you have questions, call our office at 1-866-237-9608 (toll free continental US).
We are currently offering FREE SHIPPING and a 60 day trial period on all our Wraps.
Product specialists are available 9:00 am to 5:00 pm Eastern Standard Time Monday to Friday.
If any question or concern arises, call us or simply send us an email at any time (we check our emails constantly all throughout the day and night.. even on holidays!). We will respond as soon as possible.
Learn more about Shoulder Surgery and Post-Surgery Recovery
Learn more about about how the Circulatory Boost TShellz Wrap® helps with the healing process.
Learn more about which is better for your rotator/shoulder injury - ice or heat
During your recovery, you will probably have to modify and/or eliminate any activities that cause pain or discomfort at the location of your soft tissue injury until the pain and inflammation settle. The more diligent you are with your treatment and rehabilitation, the faster you will see successful results!
Please be aware that this information is neither intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. CALL YOUR HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IMMEDIATELY IF YOU THINK YOU MAY HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider before using any of our outstanding products to make sure they're right for you and your condition or if you have any questions regarding a medical condition. Always see your doctor for a proper diagnosis as there are often many injuries and conditions (some very serious) that could be the cause of your pain.
© 2025 In.Genu Design Group, Inc. Contact Us